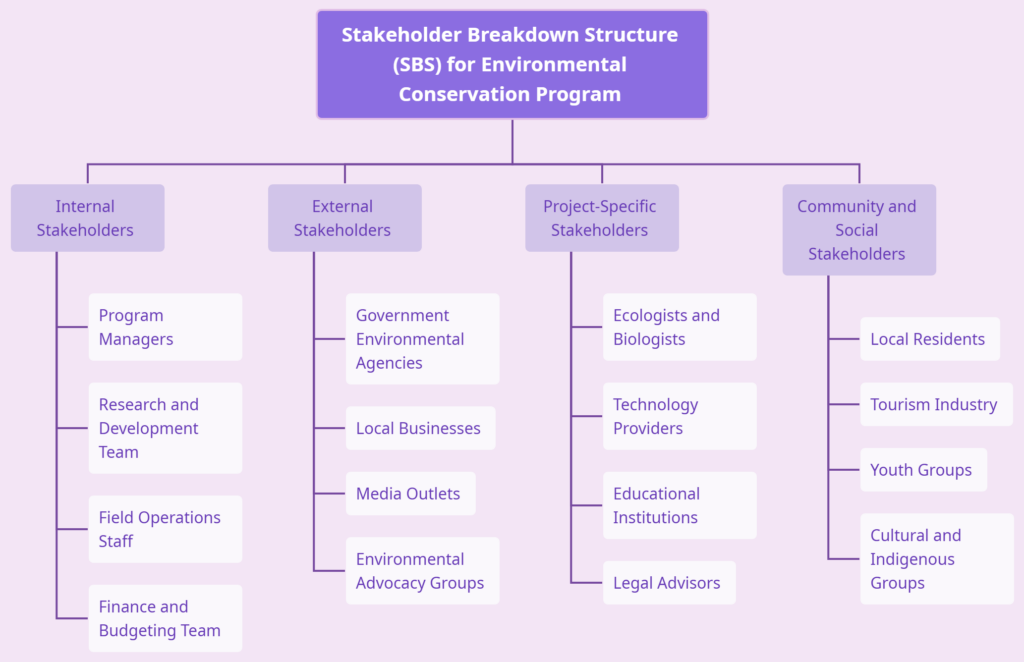
Visualizing Stakeholders with SBS for Environmental Programs
The Stakeholder Breakdown Structure (SBS) for Environmental Conservation Program intricately maps out the diverse groups and individuals involved in implementing an environmental conservation initiative. Internally, the program relies on stakeholders such as program managers, research and development teams, field operations staff, and finance and budgeting teams, who collectively steer the program’s strategic vision and operational facets. Externally, the SBS identifies government environmental agencies, local businesses, media outlets, and environmental advocacy groups as vital stakeholders whose collaboration is essential for the program’s success. Additionally, project-specific stakeholders, including ecologists and biologists, technology providers, educational institutions, and legal advisors, bring specialized expertise crucial for effective conservation efforts. Recognizing the importance of community and social stakeholders, the SBS includes local residents, the tourism industry, youth groups, and cultural and indigenous groups, underscoring the program’s commitment to engaging and respecting the diverse communities affected by environmental conservation efforts. This breakdown structure provides insights into the intricate web of relationships and collaborations necessary for the holistic success of an environmental conservation program.
Crucial Role of Stakeholder Breakdown Structure
The Stakeholder Breakdown Structure (SBS) serves as a strategic compass, offering numerous benefits for our work. Firstly, the SBS provides a systematic and visual representation of the intricate network of stakeholders involved, allowing for a comprehensive understanding of their roles, interests, and influence on the project. This clarity fosters effective communication and collaboration, aligning diverse stakeholders towards common goals. Secondly, by categorizing stakeholders into internal, external, project-specific, and community groups, the SBS enables tailored engagement strategies for each category, ensuring that the unique needs and expectations of different stakeholders are acknowledged and addressed. This tailored approach enhances stakeholder satisfaction and commitment to the project. Additionally, the SBS aids in risk identification and management by highlighting potential conflicts, enabling proactive mitigation measures. In essence, the Stakeholder Breakdown Structure acts as a powerful tool, guiding project managers in navigating the complex landscape of stakeholders, fostering collaboration, and ultimately contributing to the success of environmental conservation initiatives.
Visualizing Stakeholders with Visual Paradigm Smart Board
Visual Paradigm Smart Board emerges as a versatile tool that empowers users to create diverse mind maps with ease and efficiency. Its intuitive interface, coupled with a range of templates, facilitates the seamless translation of complex structures into visually engaging representations. Among the myriad applications, the Stakeholder Breakdown Structure (SBS) becomes a pivotal asset in strategic planning. Through Visual Paradigm Smart Board, users can visualize and organize the intricate web of stakeholders involved in various projects, such as environmental conservation initiatives. The SBS, when created using this platform, provides a dynamic and collaborative space to categorize stakeholders, understand their relationships, and plan engagement strategies effectively.